
Kalix Developer
Quickly find the latest developer content and resources.
The Kalix
Developer Experience
package com.example.shoppingcart;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnore;
public record ProductStock(Integer quantity){
public static ProductStock empty(){
return new ProductStock(null);
}
@JsonIgnore
public boolean isEmpty(){
return quantity == null;
}
}How Kalix Works
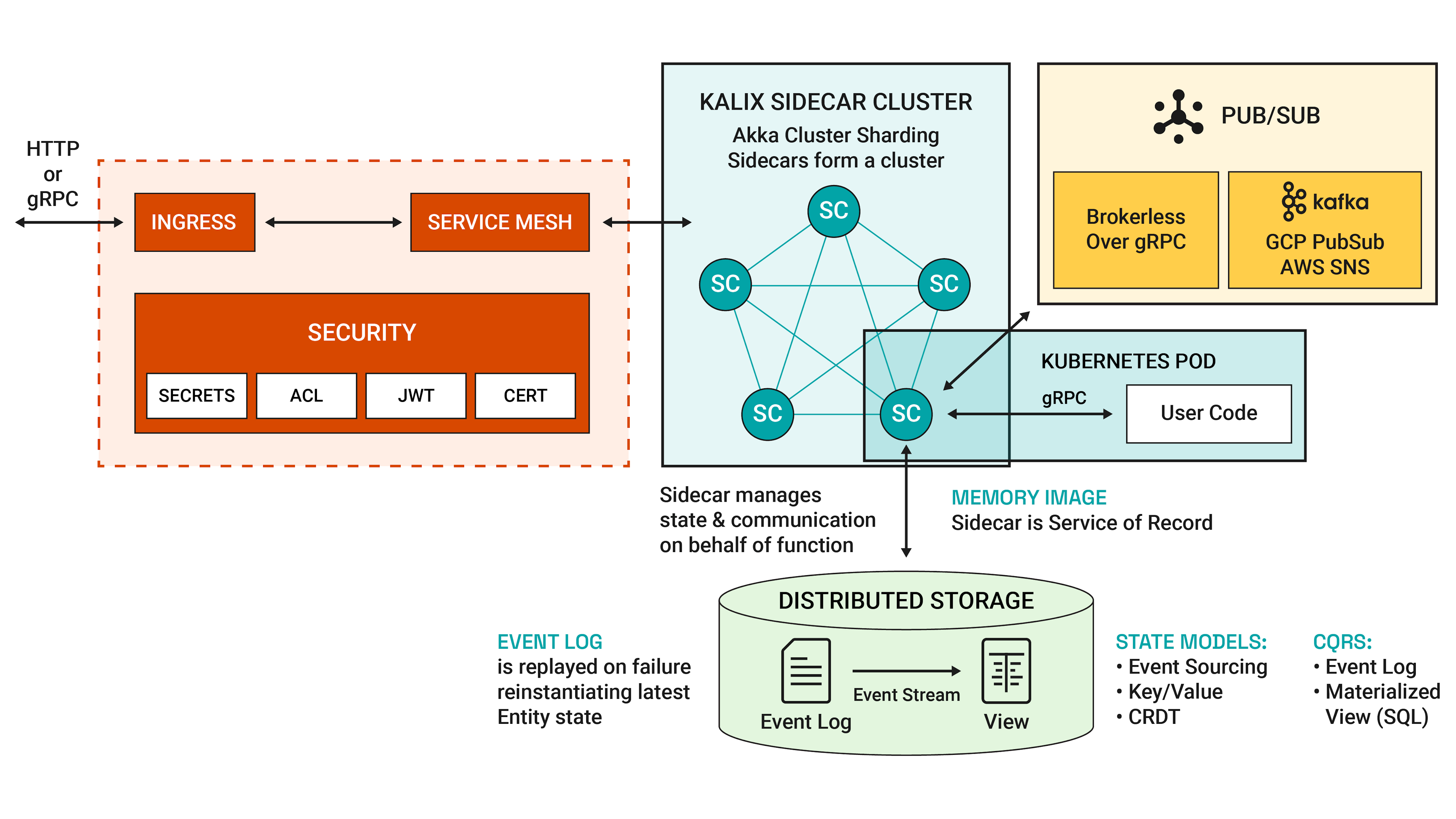 View the Infographic
View the InfographicFeature Overviews
Introducing Kalix Control Tower
Monitor all Kalix services, at a glance, and get metrics on how they are performing, their health, when they fail, etc., with Control Tower.
Introducing Kalix Container Registry
Kalix unveiled a built-in Container Registry that makes it smoother and easier to deploy a service since the registry is already set up for use.
Introducing Kalix Workflows
Both seasoned and novice developers can now quickly and easily model complex business processes or Saga-Patterns with Kalix Workflows.
How Tos
How to Install the Kalix CLI on Windows
In this tutorial, you will learn how to Install Kalix CLI on Windows.
How to Install the Kalix CLI on macOS
In this tutorial, you will learn how to Install Kalix CLI on macOS.
How to Install the Kalix CLI on Linux
In this tutorial, you will learn how to Install Kalix CLI on Linux.
Blogs
Reducing Complexity with Kalix
By Noah Barnes
Infrastructure management and database operations can be tedious, here we will cover insight into how our SREs handle Kubernetes and database management for you.
Maximizing Feature Development: Rethinking the 80/20 Ratio in Cloud Applications
By Hugh McKee
Building and running custom enterprise backend applications in the cloud requires significant time, effort, and costs that go beyond just designing and developing features.
Kalix and the Rise of Enterprise-Ready Fully Serverless Platforms
By Hugh McKee
This post dives into what constitutes a fully serverless platform, its key benefits compared to traditional serverless approaches, useful applications, and some challenges to consider.
Webinars
Building Choreography Sagas in Kalix
By Renato Cavalcanti
In this webinar, we will explore how to implement an event-driven Choreography Saga in Kalix using Kalix Entities and Action Subscriptions.
Building Orchestration Sagas with Kalix Workflow
By Renato Cavalcanti
This webinar will delve into the process of crafting an efficient Orchestration Saga in Kalix, taking advantage of Kalix Workflows.
Seamless Local Development and Swift Feedback Cycles with Kalix
By Eduardo Pinto
In this webinar, we will delve into the recent enhancements in Kalix, showcasing its features that expedite the application building and deployment process.
 Slack Channel
Slack Channel